Ptt Intrinsic Pathway : Unexpected Isolated Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time Prolongation A Practical Mini Review Rasmussen 2020 European Journal Of Haematology Wiley Online Library _ The test is conventionally used for assessing the contact factor (intrinsic) pathway of blood coagulation, and thus for screening deficiencies in this pathway, most typically factors viii, ix, and xi.
Ptt Intrinsic Pathway : Unexpected Isolated Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time Prolongation A Practical Mini Review Rasmussen 2020 European Journal Of Haematology Wiley Online Library _ The test is conventionally used for assessing the contact factor (intrinsic) pathway of blood coagulation, and thus for screening deficiencies in this pathway, most typically factors viii, ix, and xi.. The activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt) assay is a very common coagulation test, used for several reasons. Patient on heparin therapy references: Normally, when you get a cut or injury that causes bleeding, proteins in your blood called coagulation factors work together to form a blood clot. When factor ii is activated by either intrinsic or extrinsic pathway, it can reinforce the intrinsic pathway by giving positive feedback to factors v, vii, viii, xi, xiii. The clot stops you from losing too much blood.
When factor ii is activated by either intrinsic or extrinsic pathway, it can reinforce the intrinsic pathway by giving positive feedback to factors v, vii, viii, xi, xiii. I, ii, v, x (clotting factors of the common pathways), and xii, xi, ix, viii (clotting factors of the intrinsic pathway). Partial thromboplastin is the substance used for this purpose. This makes factor xii less critical; At this point, further investigation is needed and warrants the use of sensitive assays for specific coagulation factors.

The ptt may be in the normal range in patients with mild factor deficiencies, especially factor ix.
Partial thromboplastin time (ptt) is used to check the intrinsic system (factors viii, ix, xi, and xii) and the common pathways (factors v and x, prothrombin, and fibrinogen). Aptt uses an activator to narrow the reference range but, ptt does not use an activator. The activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt) assay is a very common coagulation test, used for several reasons. Intrinsic pathway is a type of blood clotting pathway which is activated by a trauma in blood or when blood is exposed to a subendothelial collagen. Patients can actually clot well without factor xii. Increased levels in a person with a bleeding disorder indicate a clotting factor may be missing or defective. The aptt is the time, in seconds, for patient plasma to clot after the addition of an intrinsic pathway activator, phospholipid and calcium. Plasma is collected and anticoagulated with citrate buffer; The test is conventionally used for assessing the contact factor (intrinsic) pathway of blood coagulation, and thus for screening deficiencies in this pathway, most typically factors viii, ix, and xi. When factor ii is activated by either intrinsic or extrinsic pathway, it can reinforce the intrinsic pathway by giving positive feedback to factors v, vii, viii, xi, xiii. Commonly used activators are kaolin, ellagic acid, glass (which is why blood clots in a red top tube) and siliceous earth (e.g. Partial thromboplastin time, activated (aptt) the activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt) is a measure of the integrity of the intrinsic and common pathways of the coagulation cascade. There are various substances that activate factor xii.
Normally, when you get a cut or injury that causes bleeding, proteins in your blood called coagulation factors work together to form a blood clot. Increased levels in a person with a bleeding disorder indicate a clotting factor may be missing or defective. It also is the best single screening test for coagulation disorders. Partial thromboplastin time (ptt) is the time it takes for a patient's blood to form a clot as measured in seconds. Aptt stands for activated partial thromboplastin time.

There are various substances that activate factor xii.
You're right about the ptt, though: Plasma is collected and anticoagulated with citrate buffer; At this point, further investigation is needed and warrants the use of sensitive assays for specific coagulation factors. The test is conventionally used for assessing the contact factor (intrinsic) pathway of blood coagulation, and thus for screening deficiencies in this pathway, most typically factors viii, ix, and xi. A phospholipid platelet substitute is added to the patient's blood to. The intrinsic pathway is clinically measured as the partial thromboplastin time (ptt). The coagulation cascade can be divided into two pathways, intrinsic and extrinsic pathways. A normal pt with an abnormal aptt means that the defect lies within the intrinsic pathway, and a deficiency of factor viii, ix, x, or xiii is suggested. Aptt uses an activator to narrow the reference range but, ptt does not use an activator. The aptt is the time, in seconds, for patient plasma to clot after the addition of an intrinsic pathway activator, phospholipid and calcium. A partial thromboplastin time (ptt) test measures the time it takes for a blood clot to form. Therefore, it checks clotting factors: Ptt (sometimes also called activated partial thromboplastin time) measures the intrinsic pathway, because two ts in the picture above are in a relationship.
At this point, further investigation is needed and warrants the use of sensitive assays for specific coagulation factors. Commonly used activators are kaolin, ellagic acid, glass (which is why blood clots in a red top tube) and siliceous earth (e.g. Ptt tests the function of all clotting factors except factor vii (tissue factor) and factor xiii (fibrin stabilizing factor). The aptt assesses the intrinsic and common pathways. Ptt measures the integrity of the intrinsic system (factors xii, xi, viii, ix) and common clotting pathways.
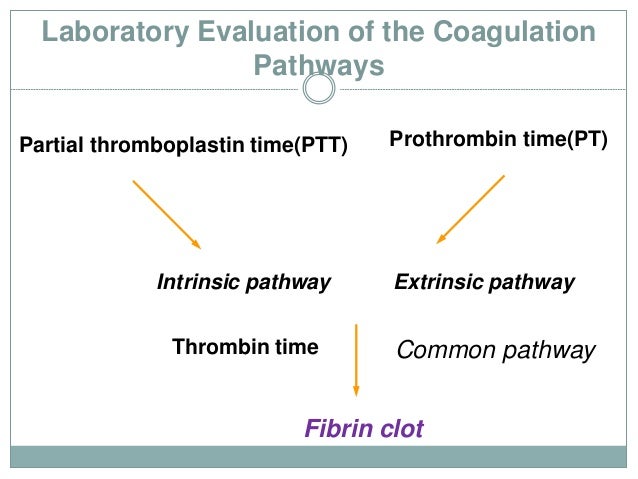
At this point, further investigation is needed and warrants the use of sensitive assays for specific coagulation factors.
A normal aptt with an abnormal pt means that. You have several coagulation factors in your blood. It is used to measure the activity of the intrinsic pathway of the clotting cascade. A deficiency of fxii is associated with longer prolongation of activated partial thromboplastin time (aptt) than that for fxi or pkk deficiency. This is because although the intrinsic and extrinsic pathways are dependent on each other (and must both work well) in the body, they are not dependent on each other in the lab. Commonly used activators are kaolin, ellagic acid, glass (which is why blood clots in a red top tube) and siliceous earth (e.g. Intrinsic pathway coagulation factor profile, aptt, partial thromboplastin time, ptt, blood coagulation tests what is this test? Harmening dh (1997) clinical hematology and fundamentals of hemostasis A partial thromboplastin time (ptt) test measures the time it takes for a blood clot to form. Plasma is collected and anticoagulated with citrate buffer; The clot stops you from losing too much blood. Aptt is used to evaluate the intrinsic and common pathways of coagulation (table 5; The ptt may be in the normal range in patients with mild factor deficiencies, especially factor ix.
The observed protection of intrinsic pathway knockouts from arterial thrombosis has led to the evaluation of numerous inhibitors of this pathway in models of thrombosis ptt. A normal pt with an abnormal aptt means that the defect lies within the intrinsic pathway, and a deficiency of factor viii, ix, x, or xiii is suggested.